Allosteric Inhibition of the Protein-Protein
Interaction Between the Leukemia-Associated Proteins RUNX1 and CBFβ.
Chemistry & Biology 2007; 14(10):1186-1197.
Numerous inhibitors of enzymatic
activity have been developed, however the development of
inhibitors of protein-protein interactions has only recently
come to the forefront as a viable approach. Allosteric
inhibition of such protein-protein interactions presents a
number of advantages, including not having to compete for
binding with the partner protein, however to date there are
very few examples of such inhibitors. We have developed novel
allosteric small molecule inhibitors of the binding of RUNX1
to CBFβ, two proteins whose translocations play a critical
role in the development of acute myeloid leukemia and acute
lymphocytic leukemia.
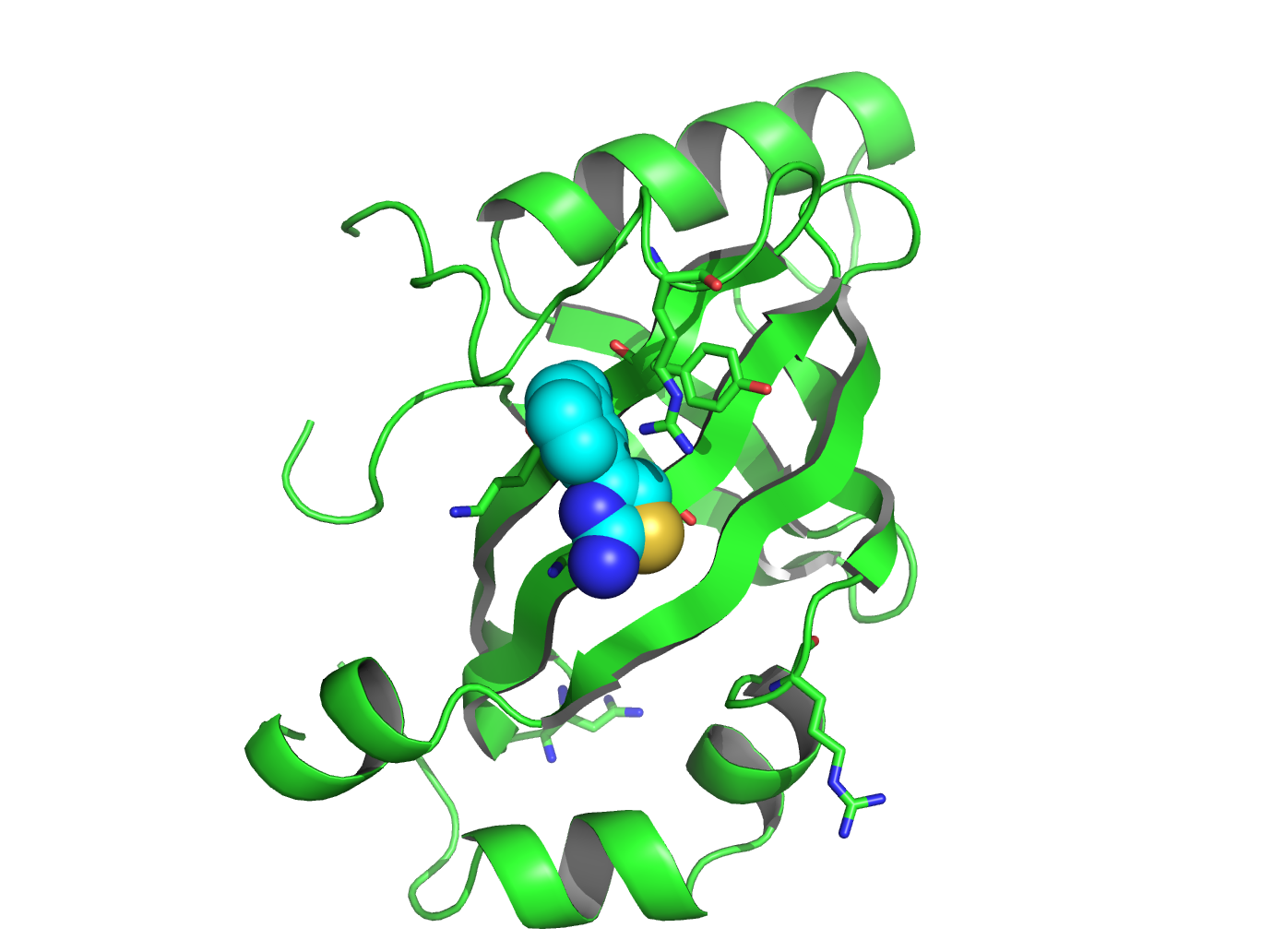
On the cover:
Combatting Leukemia: RUNX1 and CBFβ Interaction Interupted
The two subunits of the heterodimeric transcription
factor core binding factor (RUNX1 and CBFβ) play
critical roles in hematopoiesis and are frequent targets of
chromosomal translocations found in leukemia. In this paper,
we describe the development of a small molecule inhibitor (red) that
binds to an allosteric site on CBFβ (blue) and
inhibits the protein-protein interaction between the RUNX1 Runt domain
(green) and CBFβ. Treatment
of the human leukemia cell line ME-1 with inhibitor results in changes
in morphology indicative of increased differentiation (cells shown at
the top half of the background) versus untreated cells (cells shown at
the bottom half of the background), providing support for this as a
potential therapeutic approach.